

Types of Railway Project
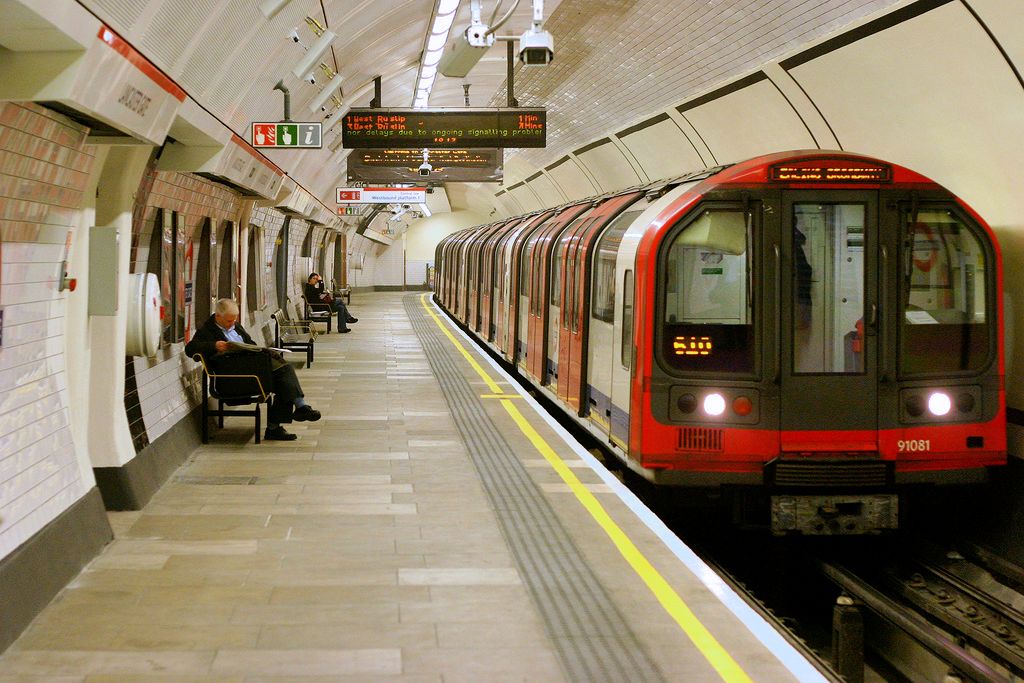
Rapid transit/Heavy rail
Rapid transit/Heavy rail - high passenger capacities and frequency of service, and full grade separation from other traffic (cars and other rail traffic). It is often known as metro, subway, Underground, MRT.

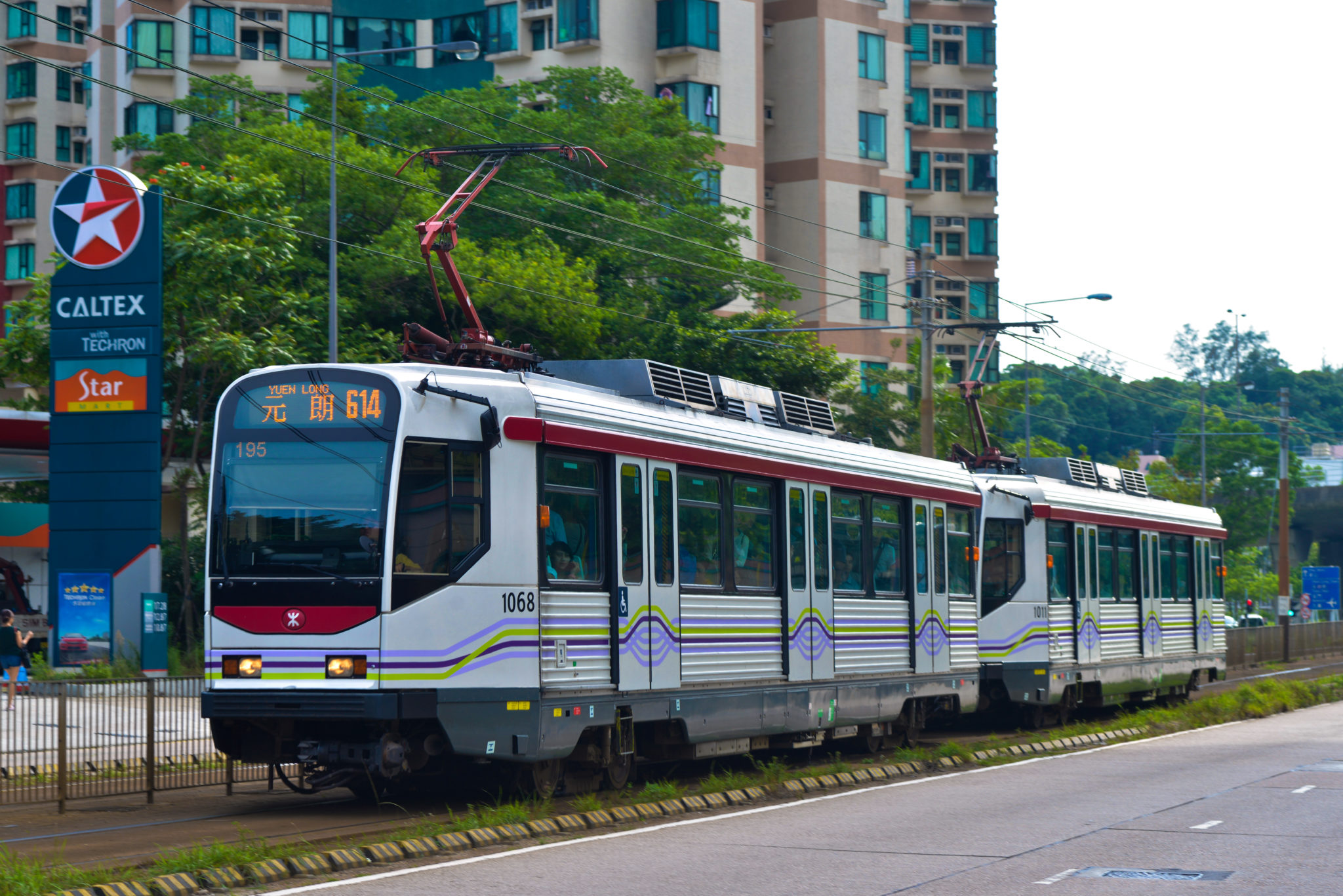
Light rail
Light rail - has higher capacity/speed than a tram and generally operates with multiple unit trains rather than single tramcars.

Commuter rail (regional rail/suburban rail)
Commuter rail (regional rail/suburban rail) - system operates on mainline trackage which may be shared with intercity rail.

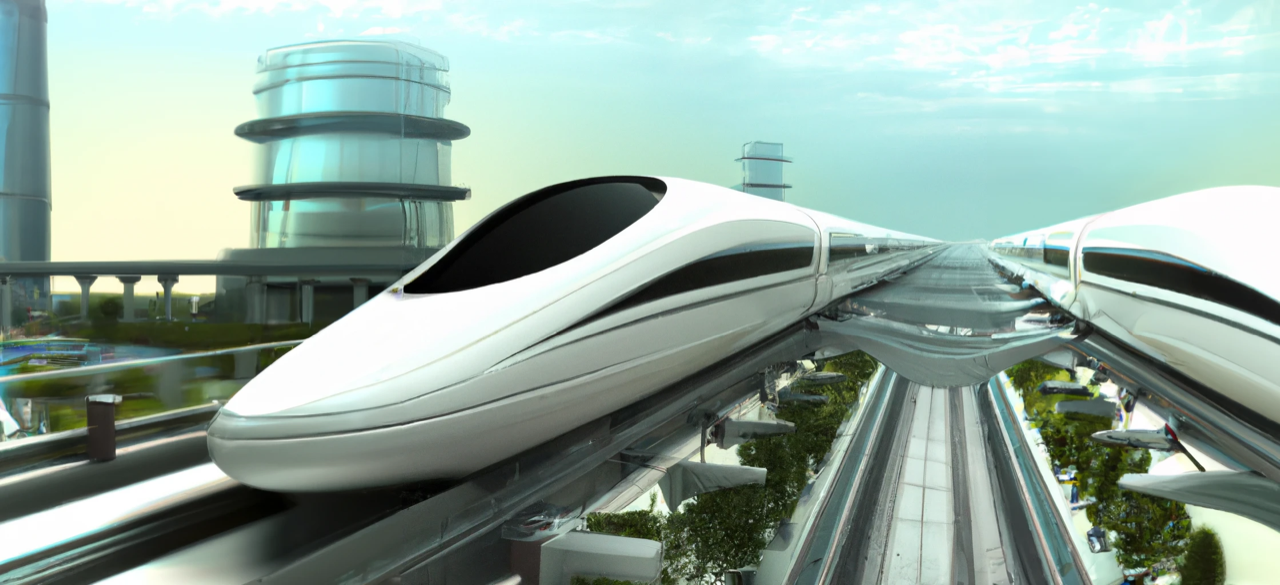
Monorail
Monorail - a railway in which the track consists of a single rail, as opposed to the traditional track with two parallel rails.

High speed trains
High speed trains - trains that operates at speeds of 125 mph (200 km/h) or faster using an integrated system of specialized rolling stock and dedicated tracks. Examples are TGV, Velaro, KTX, Shinkansen and so on.

Inter-city trains
Inter-city trains - trains traveling long distances (longer than commuter or regional trains) connecting metropolitan areas. Companies include China Railways, Indian Railways, InterCity, JR Group, Korail and so on.


Types of Rolling Stock
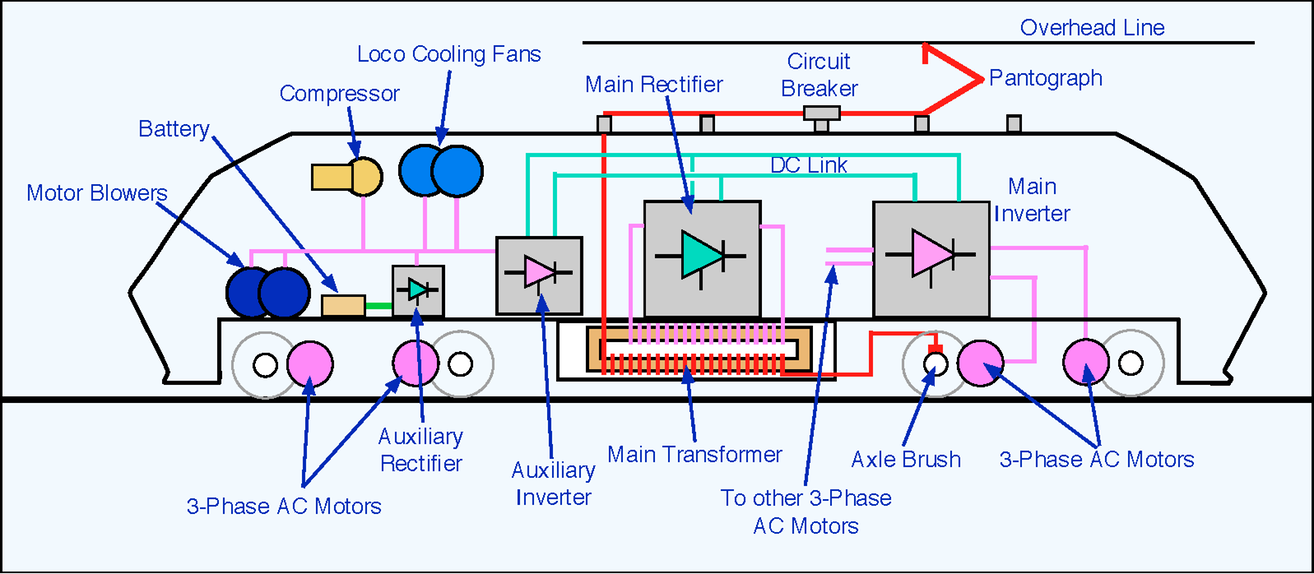
Electric locomotives
Pantograph - The current collection system used by locomotives to electrify from overhead lines.
Inverter – Electronic power device mounted on trains to convert DC to AC (provide AC).
Rectifier - A converter consisting of thyristors and diodes which is used to convert AC to DC. Types of rolling stock
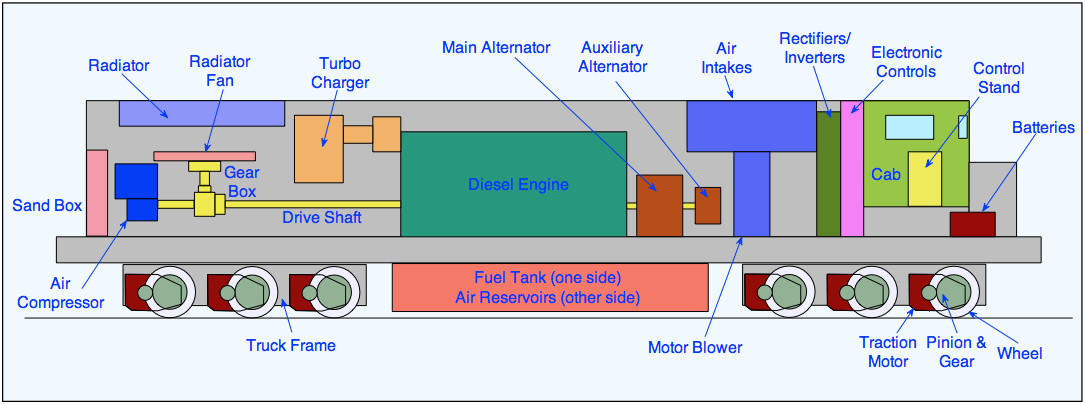
Diesel locomotives
Blower motor – blow cold air within HVAC systems.
Alternator – It generates AC electricity which is used to provide power for the traction motors mounted on the trucks and Auxiliary Alternator is used for lighting, air conditioning, facilities and so on.
Turbo Charging - it is used to increase the amount of air pushed into each cylinder, so that it will get more power out of its ignition. It is driven by exhaust gas from the engine.
Types of Fixed Stock
Electric Traction Power for Electric locomotives

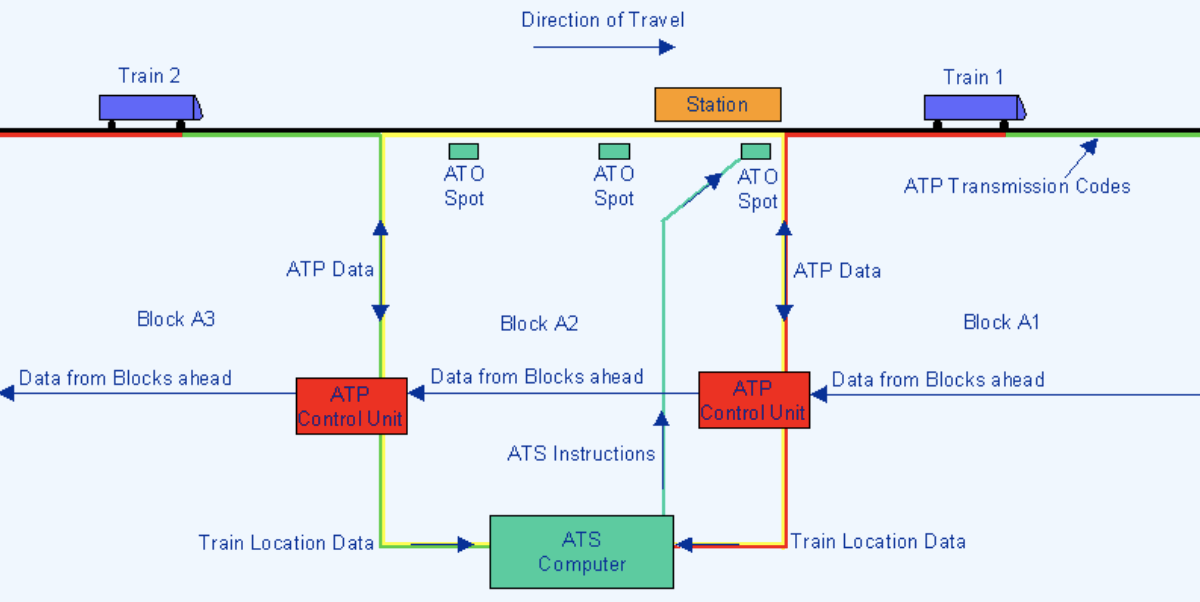
Train signaling
ATP (Automatic Train Protection) – give a Limit of Movement Authority (LMA).
ATO (Automatic Train Operation) – driving part of the operation (accelerates and stops)
ATS (Automatic Train Supervision) - determine if the train is running according to schedule
4
Recent CommentsMichael Busch
1 week agoDummy comment - But I must explain to you how all this mistaken idea of denouncing pleasure and praising pain was born and I will give you a complete account of the system, and expound the actual teachings.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
OTHER SECTORS YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN