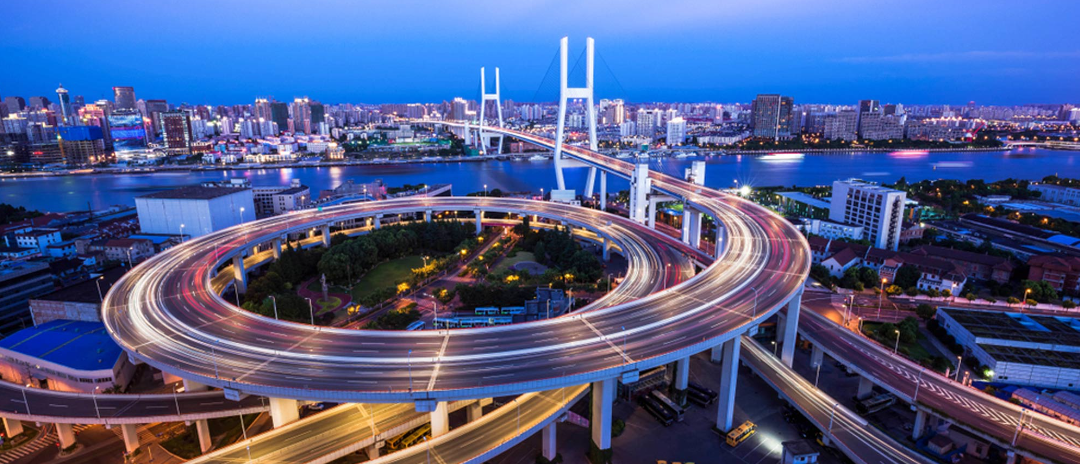


What is Road Project?
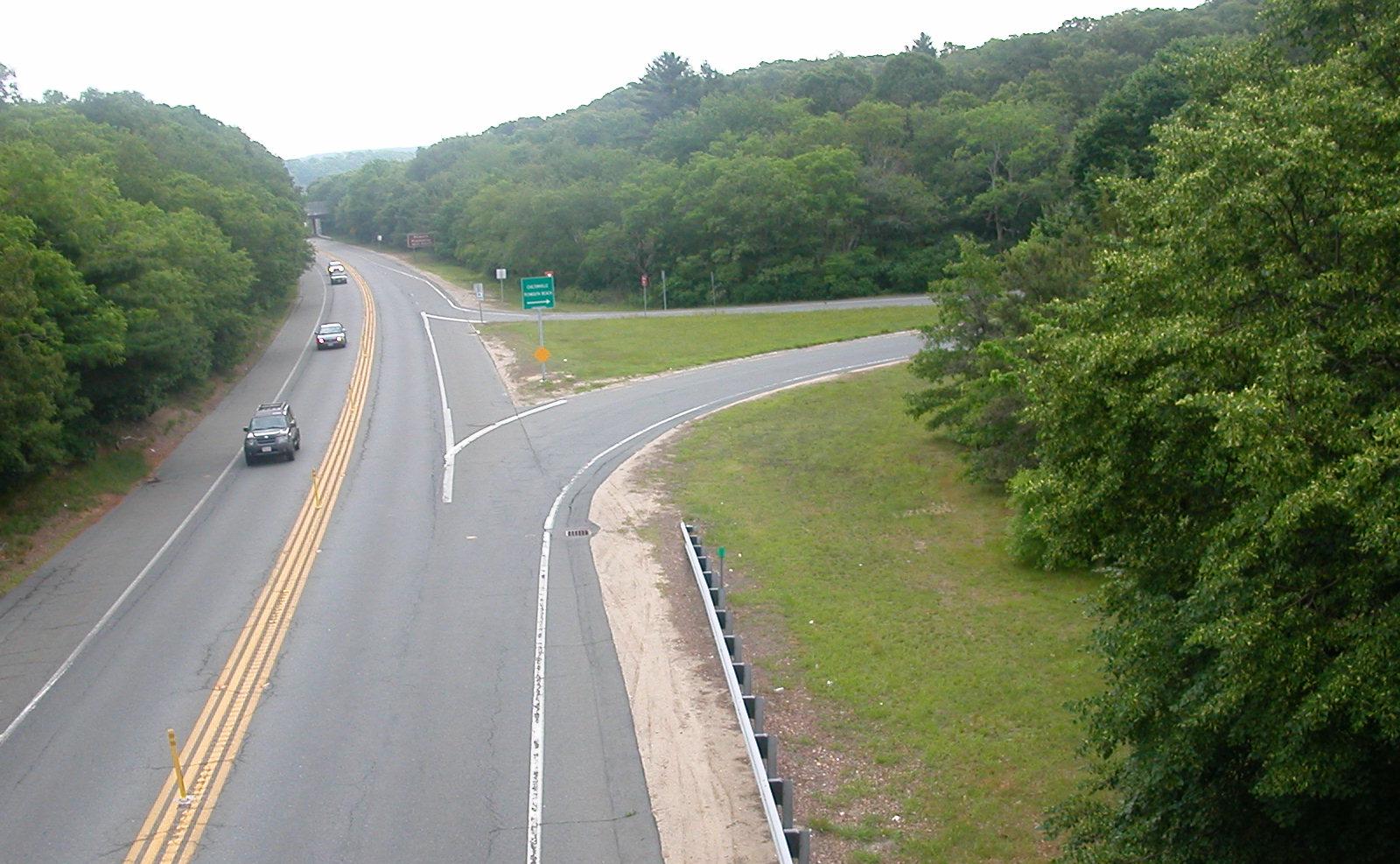

Two-lane highways

Expressway (Limited-access road)
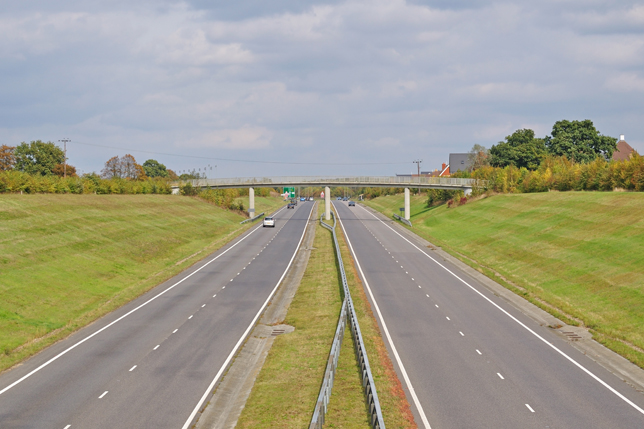

Dual carriageway
Types of Road Projects
Two-lane highways - These are the usual single carriageways. Traffic on two-lane highways normally flow in opposite direction on single lane. Two-lane highways may be rural, urban or intercity roads.
Expressway (Limited-access road) - high-speed traffic which has many or most characteristics of a controlled access highway. Examples are Autobahn, Autostrada Freeway, Motorway and so on.
Dual carriageway - carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation. Used in Ireland, Singapore, UK, US and so on.

Material types for Road Projects
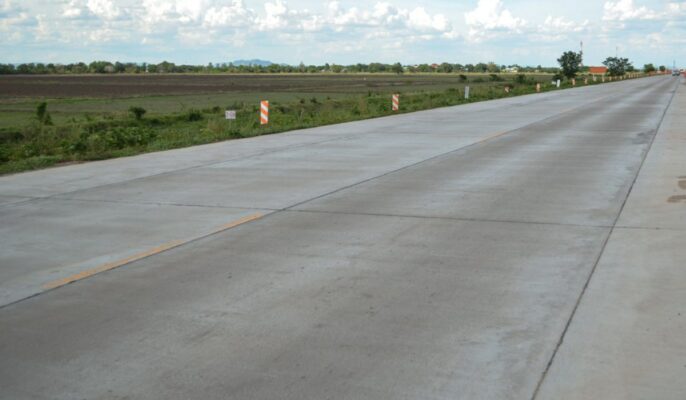
Concrete roads
Composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement.

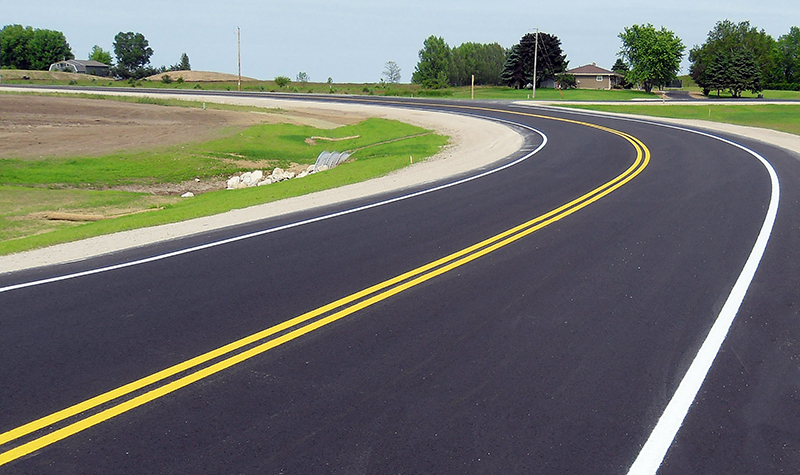
Asphalt Roads
Asphalt consists of mineral aggregate bound together with asphalt, laid in layers, and compacted. Asphalt examples are Hot-mix asphalt (HMA), Warm-mix asphalt (WMA), Cold-mix asphalt, Mastic and High-modulus asphalt.

Gravel Roads
Type of unpaved road surfaced with gravel that has been brought to the site from a quarry or stream bed. They are common in less-developed nations. Material types for Road Projects


Type of Bridge Project?
Suspension Bridge
Suspension bridge - the roadway is suspended by cables from two tall towers. Most of the weight is supported by the two towers. Suspenders run vertically from the deck up to the main supporting cables.

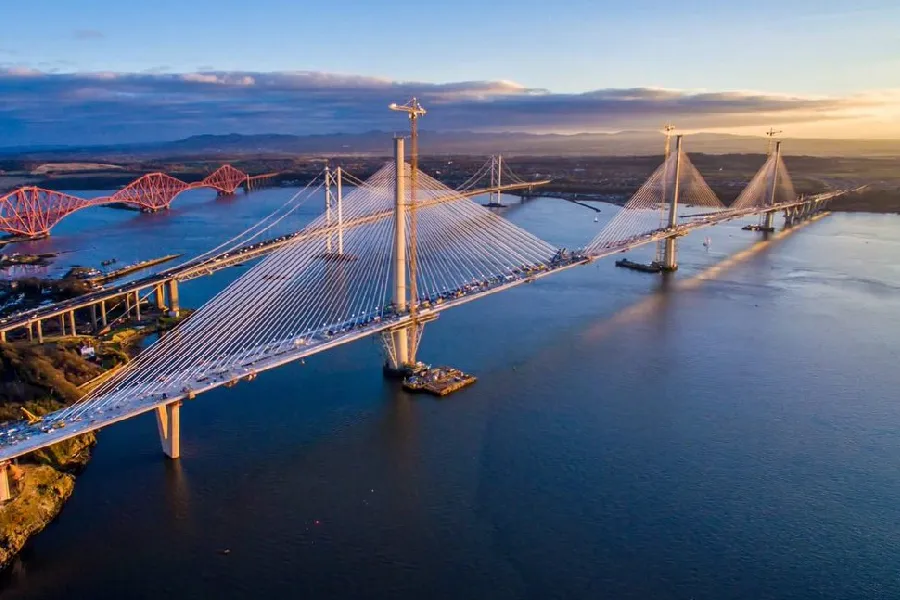
Cable-Styled Bridge
Cable-stayed bridge - Cables are connected from the pylons to the deck below. There are harp design (connect to different points) and fan design (connect to one point).

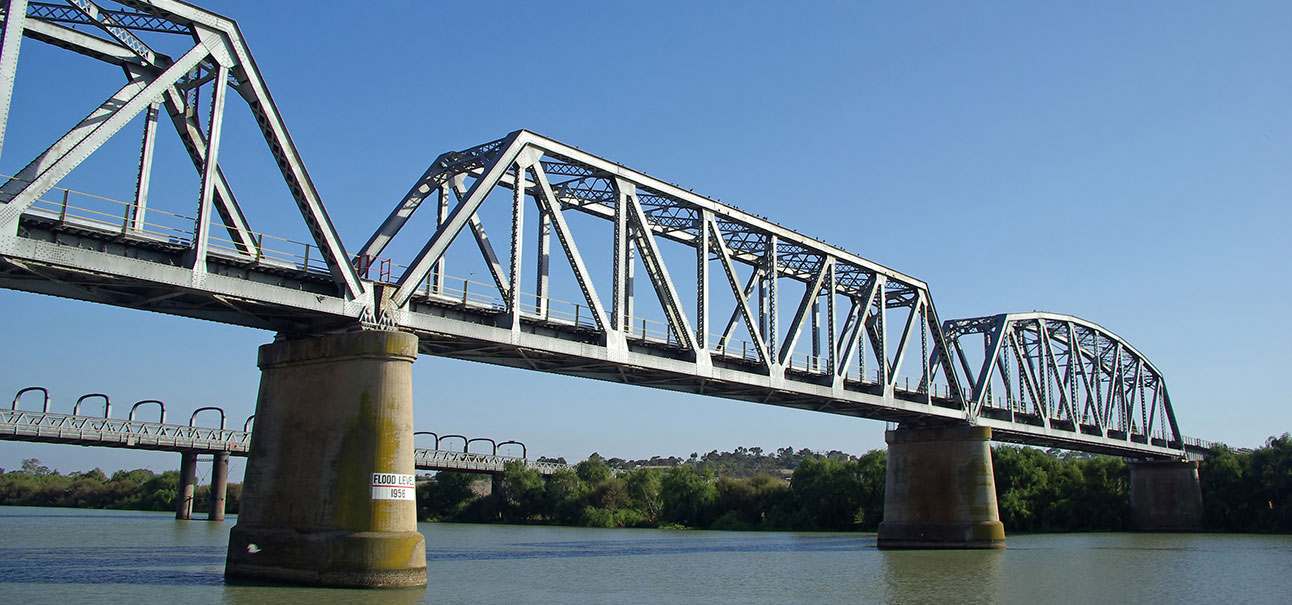
Truss Bridges
Truss bridges - uses a diagonal mesh. Triangle-shaped posts above the bridge to distribute forces across almost the entire bridge structure.

Beam Bridge
Beam Bridge - simply supported structure, with two beams running between abutments/piers.

Arch Bridge
Arch Bridge - it has abutments used for supporting the curved arch structure from above the bridge.
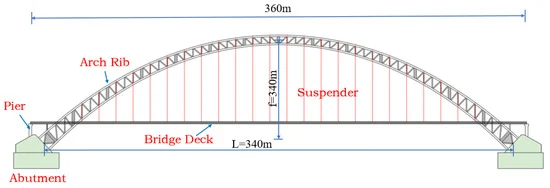
Tied Arch Bridge
Tied Arch Bridge - arch structure supported by vertical ties between the arch and the deck.
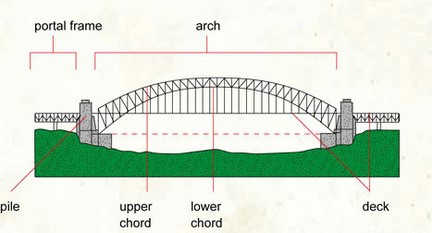
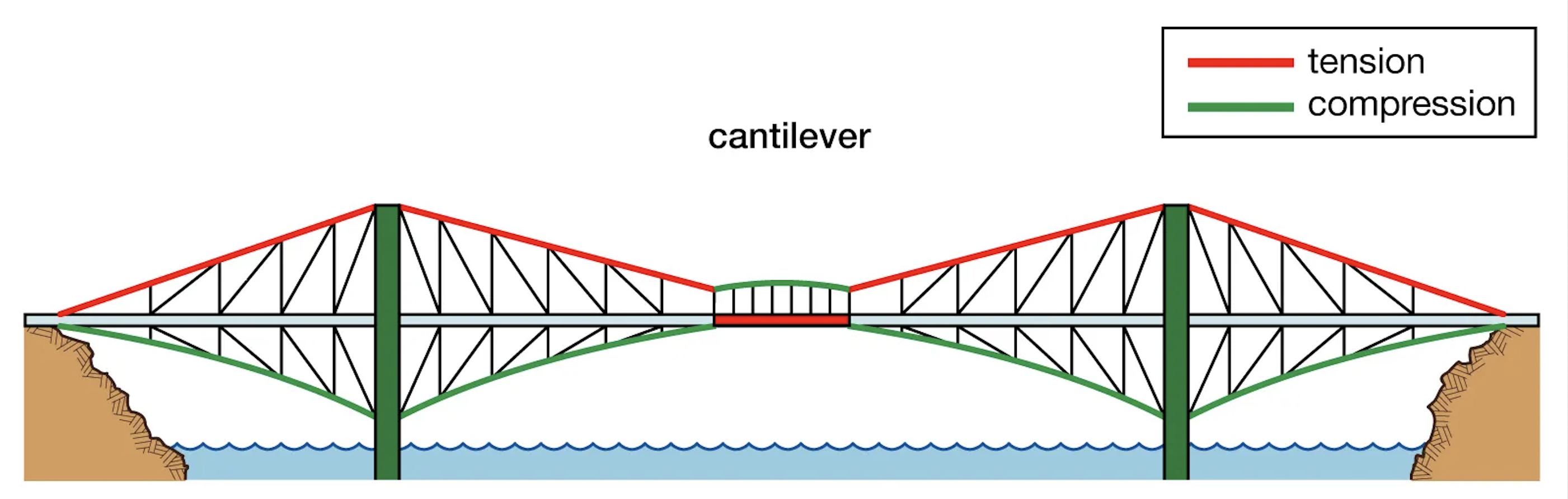
Cantilever Bridge
Cantilever Bridge - cantilevers, which are horizontal structures supported only on one end.
4
Recent CommentsMichael Busch
1 week agoDummy comment - But I must explain to you how all this mistaken idea of denouncing pleasure and praising pain was born and I will give you a complete account of the system, and expound the actual teachings.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
OTHER SECTORS YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN