


What is a Water Plant Project?
Definition of Desalination and Reverse Osmosis (RO)
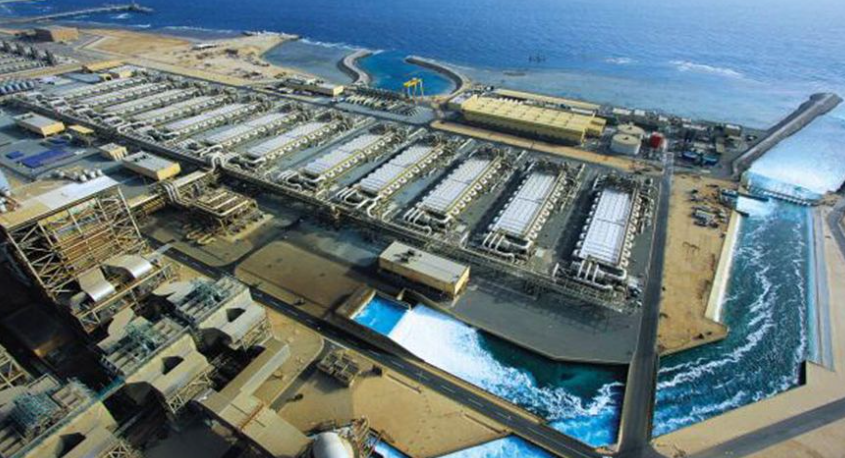
A desalination plant removes salt and impurities from seawater (or raw water) to produce drinkable water
A Reverse Osmosis (RO) system uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove salts, organic material, colloidal particles, and bacteria from feed water, producing fresh, desalinated water.
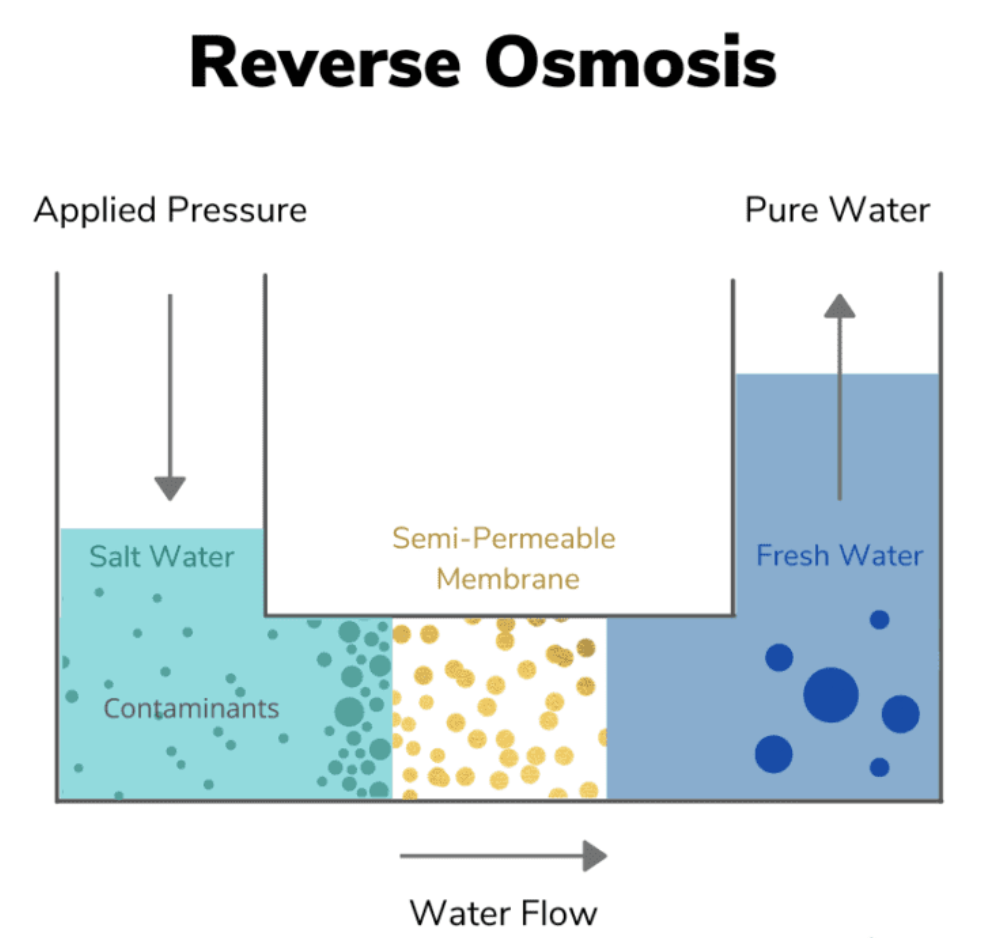
Traditional RO(Reverse Osmosis) Water Treatment plant
Desalination plants are often called RO (Reverse Osmosis) Water Treatment plants, and their primary role is to remove salt from water.
HPP: High-Pressure Pump, BP: Booster Pump, ERD: Energy Recovery Devices
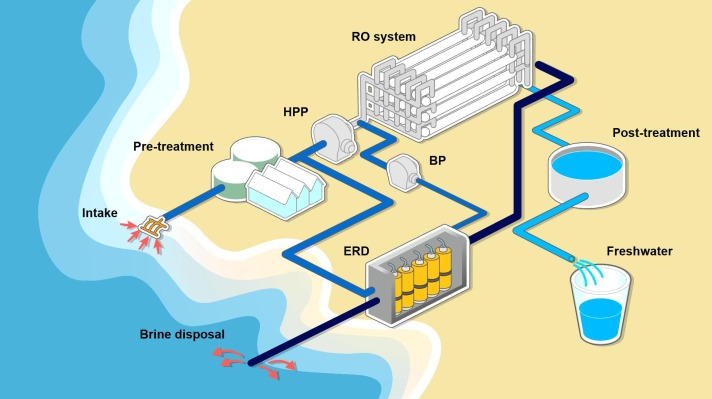
Types of Water Treatment Plant Process (RO, DAF, DMF, UF, GAC, etc)
RO : Reverse Osmosis, DAF : Dissolved Air Floatation, DMF : Dual Media Filtration, UF : Ultra Filtration, GAC : Granular Activated Carbon
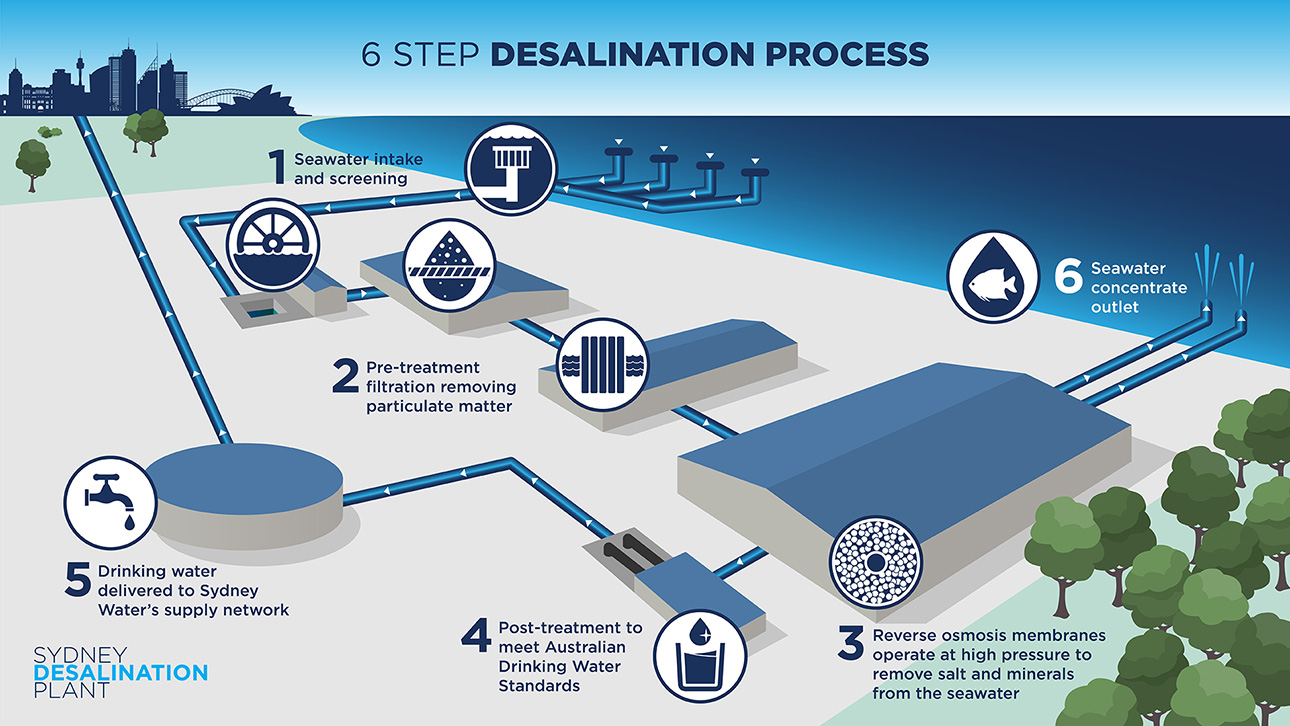
Desalination Water Plant
A desalination water plant is a facility designed to remove salts and other impurities from seawater or brackish water to produce fresh, potable water suitable for human consumption and various other uses.
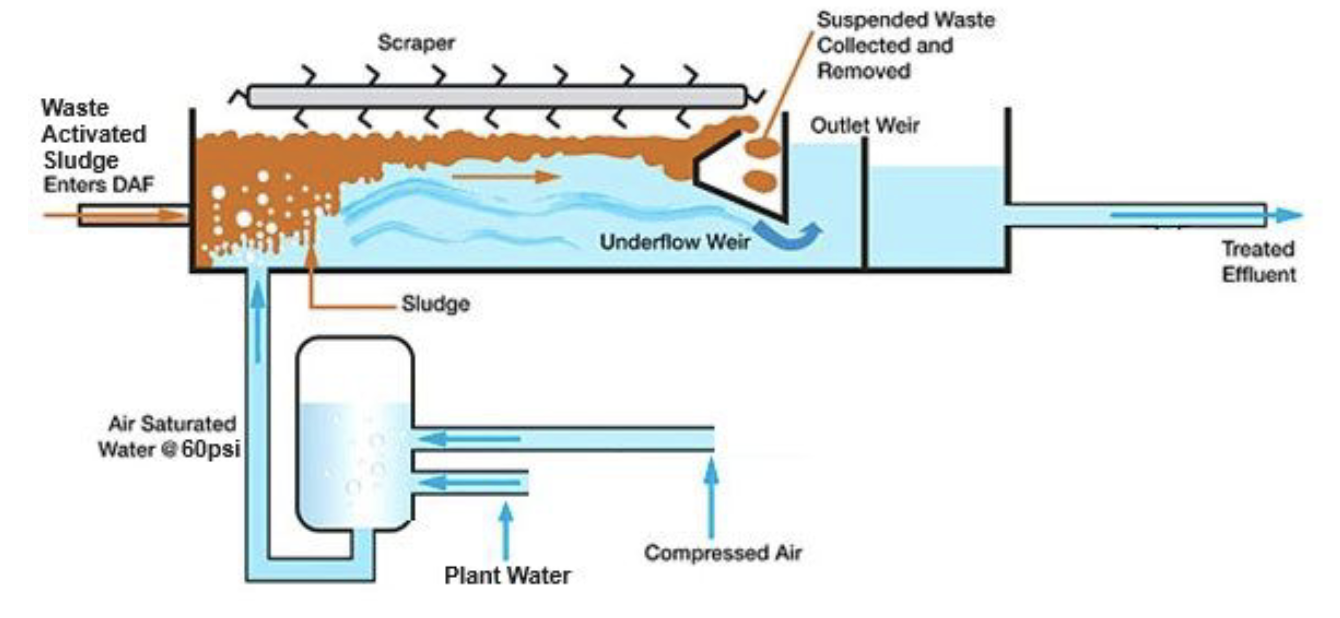
Dissolved Air Floatation
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process designed to remove suspended solids, oils, and other impurities from water and wastewater.
It is particularly effective for treating industrial and municipal wastewater that has a high concentration of particulate matter.
The DAF process uses air bubbles to float suspended particles to the surface, where they can be removed efficiently.
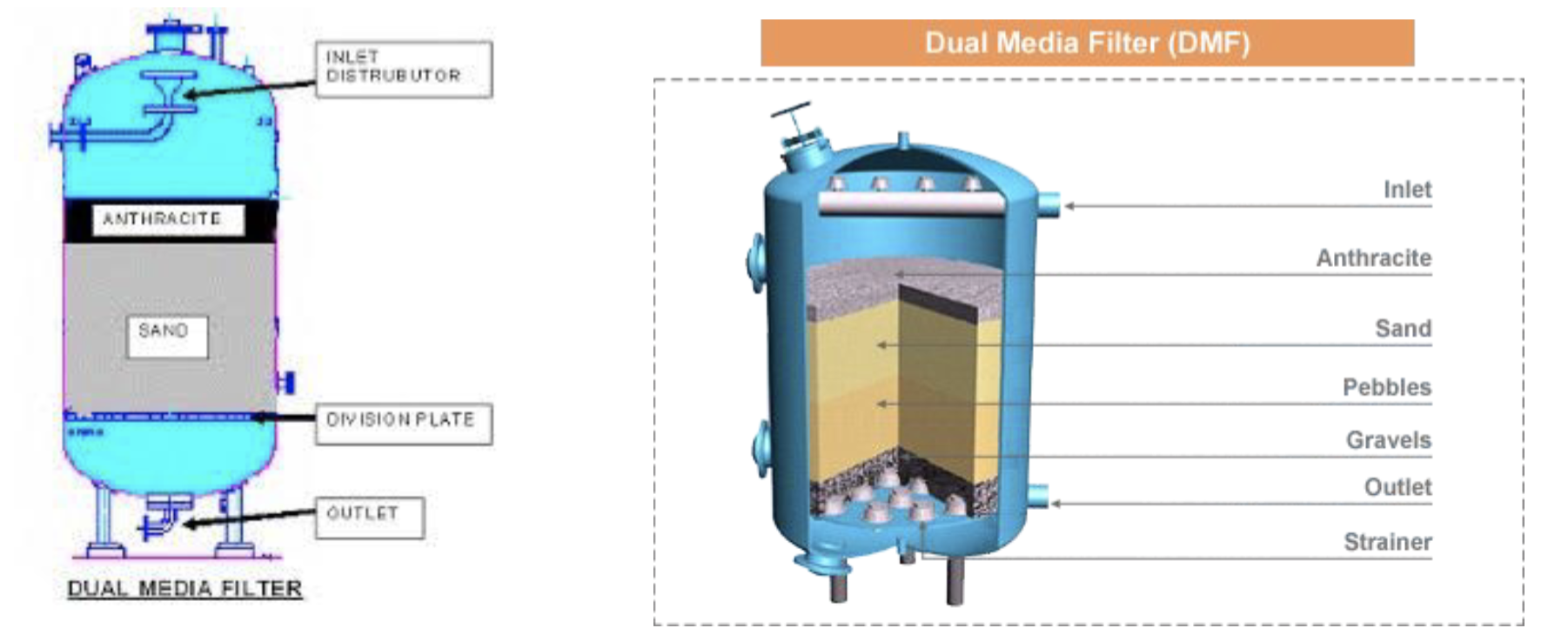
Dual Media Filtration
A Dual-Media Filter is a type of filtration system used in water treatment to remove particulates and contaminants. It employs two distinct layers of filter media to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the filtration process.
Granular Activated Carbon
Granular activated carbon (GAC) generally is an organic carbon filtration media — wood, coconut shells, coal or peat — used for water purification, typically applied in a fixed bed application.

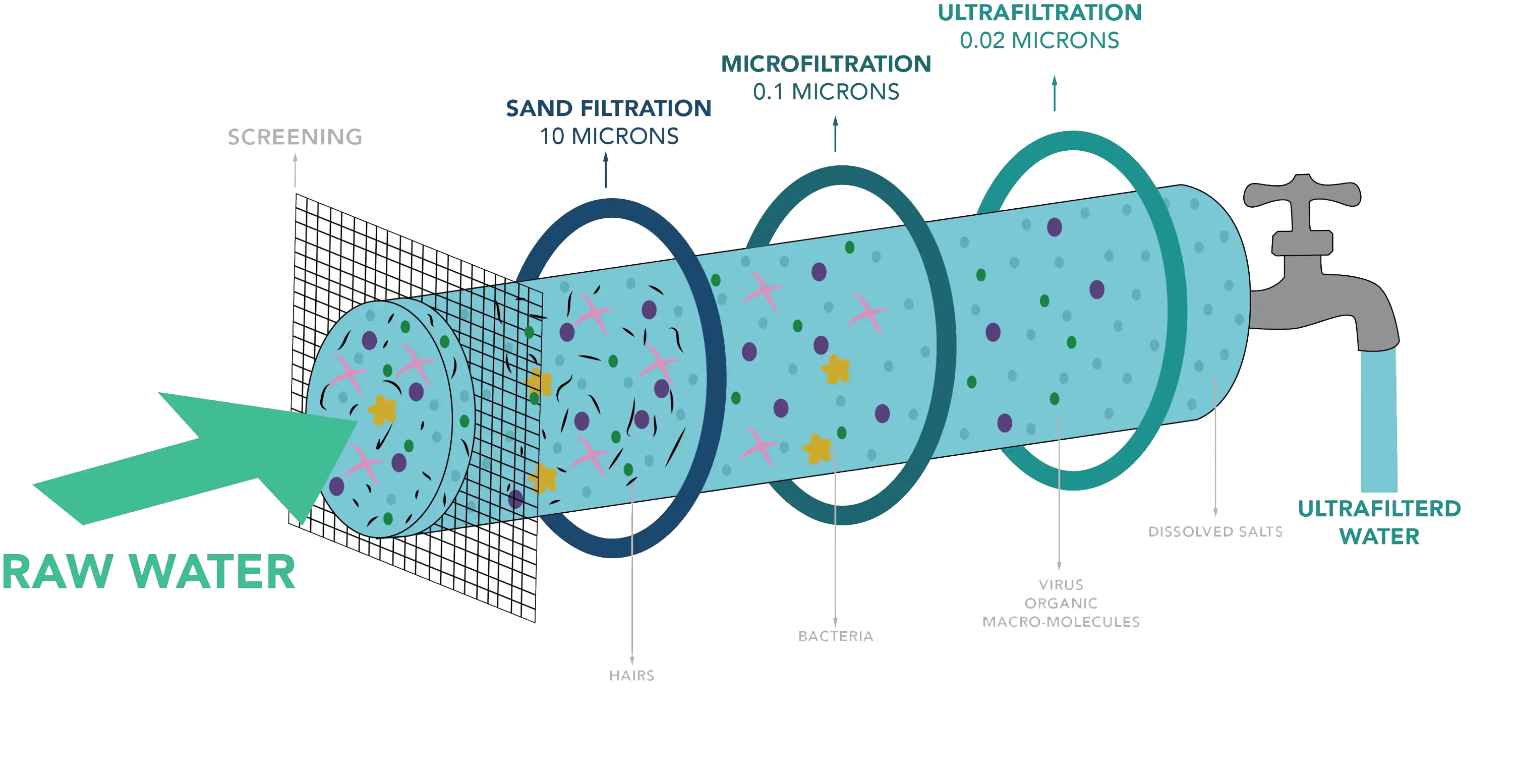
Ultra Filtration
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a membrane filtration process similar to Reverse Osmosis, using hydrostatic pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane. The pore size of the ultrafiltration membrane is usually 103 - 106 Daltons.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a pressure-driven barrier to suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, endotoxins and other pathogens to produce water with very high purity and low silt density.
Who owns Water Plants?
Water Utility
The ownership structure of a water utility typically falls into one of several categories: public (municipal), private (investor-owned), or cooperative (customer-owned), with hybrid public-private partnerships also prevalent.
IWP
An Independent Water Producer (IWP) is a private entity or company that is involved in the production of water, typically through the construction and operation of water treatment facilities, without being a part of a public water utility.
IWPs often focus on supplying water to municipalities, industries, or other entities under long-term agreements.
EPC Contractor
An EPC Contractor (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction Contractor) is a company that provides a comprehensive package of services for the design, pro- curement, and construction of projects, often in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, water treatment, and infrastructure.
EPC contractors manage the entire lifecycle of a project from initial concept to completion and handover.
4
Recent CommentsMichael Busch
1 week agoDummy comment - But I must explain to you how all this mistaken idea of denouncing pleasure and praising pain was born and I will give you a complete account of the system, and expound the actual teachings.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
Albert Flores
1 week agoTF-IDF Content Optimisation: Your Guide to an Underappreciated SEO Concept
In mauris porttitor tincidunt mauris massa sit lorem sed scelerisque. Fringilla pharetra vel massa enim sollicitudin cras. At pulvinar eget sociis adipiscing eget donec ultricies nibh tristique.
3
OTHER SECTORS YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN